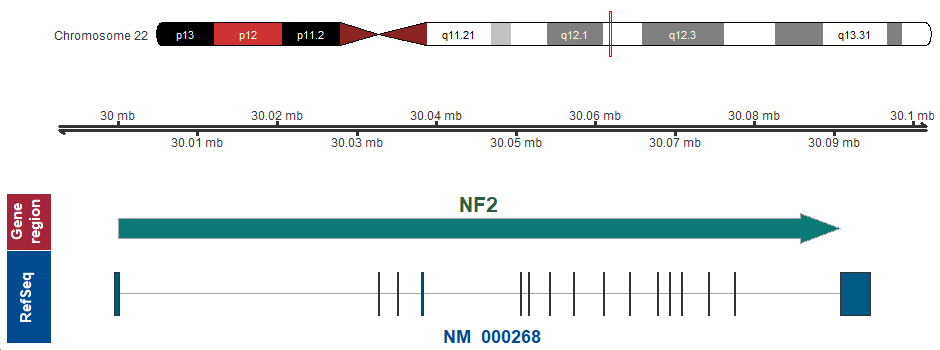
Missense variant interaction scanning reveals a critical role of the FERM domain for tumor suppressor protein NF2 conformation and function | Life Science Alliance

In vitro antisense therapeutics for a deep intronic mutation causing Neurofibromatosis type 2 | European Journal of Human Genetics

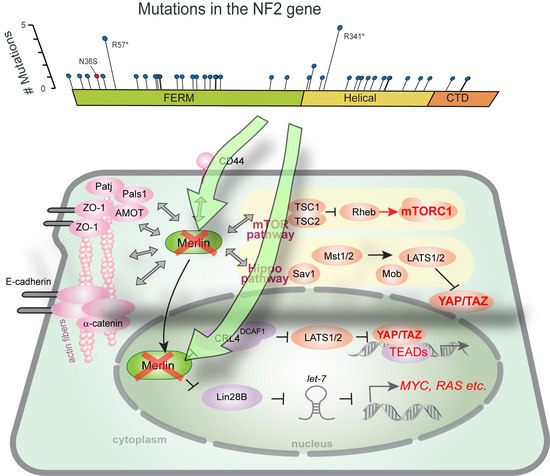
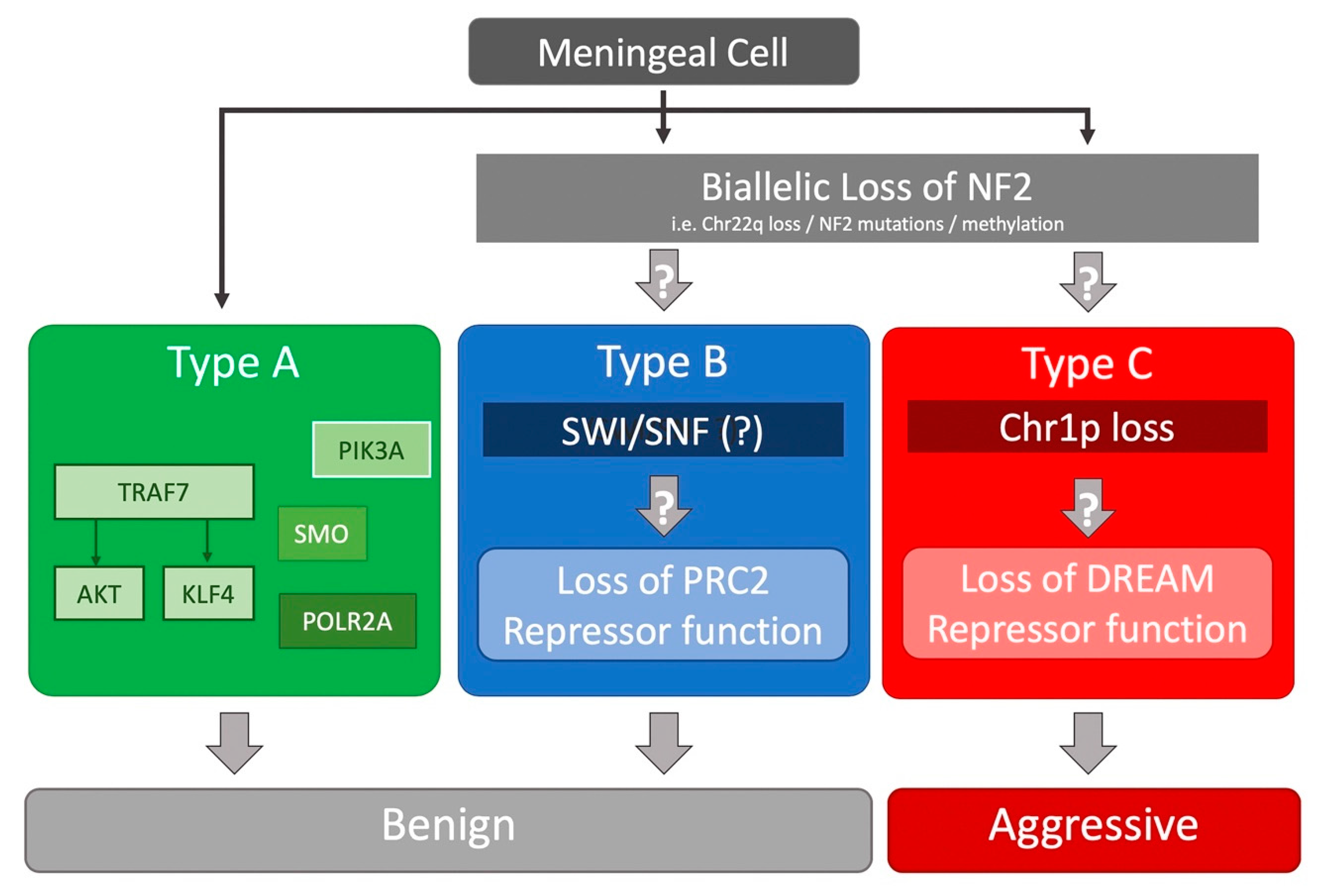
The genetic landscape and possible therapeutics of neurofibromatosis type 2 | Cancer Cell International | Full Text

The NF2 gene product merlin is a key tumor suppressor protein. The NF2... | Download Scientific Diagram

The NF2 tumor suppressor gene product, merlin, mediates contact inhibition of growth through interactions with CD44

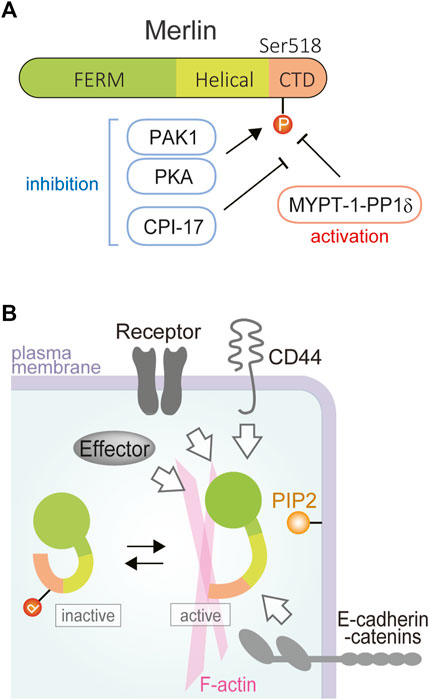
Nf2/Merlin: a coordinator of receptor signalling and intercellular contact | British Journal of Cancer

Point mutation in the NF2 gene of HEI-193 human schwannoma cells results in the expression of a merlin isoform with attenuated growth suppressive activity. - Abstract - Europe PMC